Competence cards - the 12 sub-areas
Read about the 12 competence areas on this page or download them in PDF
User competencesCompetences to be able to use the digital solutions, systems, programmes and tools necessary for your work
You may need to be a competent user in e.g:
|
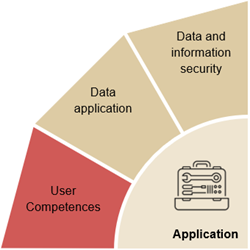  |
Data applicationCompetences to have an overview of data:
You may need to:
|
|
Data and information securityCompetences to handle data in a good and responsible way
It is necessary to have knowledge about:
|
|
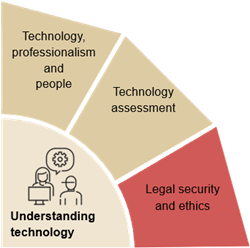
Technology, professionalism and peopleCompetence to assess digitalisation in relation to professionalism and the people who encounter your professionalism
It is necessary to be competent to do so:
|
|
Technology assessmentCompetences to assess the process of the task and from this which technologies could be relevant
It is necessary to have:
|
|
Legal security and ethicsCompetences to recognise the legal and ethical perspectives of what technologies bring
It is necessary to have:
|
|
Digital communication 1:manyCompetences to communicate to many users -e.g.via websites, LinkedIn, X
It may be necessary to have:
|
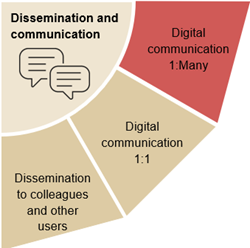 |
Digital communication 1:1Competences to communicate one-to-one via various digital channels -e.g.emails, chat, Teams
It may be necessary to:
|
 |
Dissemination to colleagues and other usersCompetences to disseminate digitalisation - what it is and how it can be used
It may be necessary to have:
|
 |
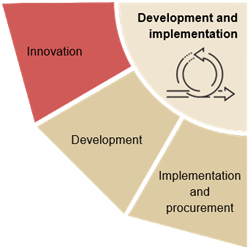
Implementation and procurementKnowledge of the methods used in procurement and implementation processes to be able to meaningfully engage in them and contribute with professionalism and experience It may be necessary to have:
|
 |
DevelopmentCompetences to have an active and guiding role in development and implementation processes
You may need to have the competences to:
|
 |
InnovationCompetences to contribute and drive the change brought about by the development and implementation of digital solutions
It may be necessary to have:
|
|